Hi everyone, I am Pepe and in this third week I have been in charge of the facilitator role of my group. This has been an exciting week because my group has worked very hard in this challenging task which we had ahead, ‘’The Treasure Hunt’’. Because of the responsibility which involves my role, I helped and encouraged each of the members of my group in each thing which was needed.
At the beginning It was not easy for me due to I did not exactly understand what we had to do in this task. But once everyone was assigned his/her role the work was easier to develop, and I was able to motivate all my group mates to carry out the activity, helping them in the search for the information.
In spite of we have to improve our coordination and efficiency working as a group, because we do not live close to each other, and because some of them have others activities in the afternoon which make difficult to choose a working schedule which suits everyone, every member of the team was committed with his/her role and made the most of their time in order to achieve the set goal. For that reason I feel proud of all my team mates for their effort.
Projections – Defining terms and recognizing patterns
A projection is the only “perfect” representation of the Earth’s surface. All maps are distorted in four major ways. The four ways maps are distorted is by the cylindrical projection, conic projection, azimuthal projection plane or polar and modificated projections of the landmasses being mapped. In order to make maps, projections must be made, and different projections require different distortions. For each projection listed below, complete the chart for the correct information.
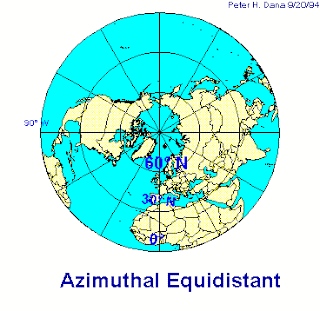
Azimuthal’s projections
1. Purpose
The Azimuthal projection or zenith projection is achieved by projecting a portion of the Earth on a planotangent to the sphere at a selected point, obtaining the vision that would be achieved either from the center of the Earth or from a point in outer space .
2. Distortion types
There are two kinds of distortions inside the planar projection, the plane and the polar types.
In planar (also known as azimuthal or zenithal) projections, the reference spherical surface is projected onto a plane.
The plane in planar projections may be tangent to the globe at a single point or may be secant. In the secant case the plane intersects the globe along a small circle forming a standard parallel which has true scale. The normal polar aspect yields parallels as concentric circles, and meridians projecting as straight lines from the center of the map. The distortion is minimal around the point of tangency in the tangent case, and close to the standard parallel in the secant case.
The polar aspect is the normal aspect of the planar projection. The plane is tangent to North or South Pole at a single point or is secant along a parallel of latitude (standard parallel). The polar aspect yields parallels of latitude as concentric circles around the center of the map, and meridians projecting as straight lines from this center. Azimuthal projections are used often for mapping Polar Regions, the polar aspect of these projections are also referred to as polar azimuthal projections.
3. Distortion- Areas that are most distorted?
This projection system has as a great advantage that the areas represented in the maps do not suffer deformation and is proportional to the original forms, they fulfill the following list: "equal surfaces represent equal solid angles"
4. Is there more than one version?
Yes. There are different types, depending on the point inside or outside of the surface area:
Perspective projections: Stereographic Projection, Ortographic Projection, Gnomonic Projection.
Non-Perspective projections: Postel Azimuthal, Equidistant projection, Lambert Azimuthal equal area projection.
5. Problems
It is limited to 90º from the center, although it can project the complete globe. The projections of polar orientation are more suitable for areas inside a radio of 30º, because the distortion is minimal. Distances and shapes in some Azimuthal projections are distorted away from the center. Distorsion increases away from point of tangency (touch point) or secancy (cut point).
6. Sociocultural implications of using it as a learning resource?
It is useful for air and sea navigation routes. In addition, as a learning resource it is well-suited for maps of the Arctic, Antarctic and hemisphere types of maps.
Mercator’s projection

1. Purpose.
This projection has been used from the century 18th for nautical letters because allowed trace the routes of constant heading or loxodromes as straight and uninterrupted lines, to difference of other projections more accurate.
2. Projection types.
There are two types of projections: the Tangent and secant equatorial aspect and the Equatorial and transverse.
Tangent and secant equatorial aspect.
The cylinder may be either tangent or secant to the reference surface of the Earth. In the tangent case, the cylinder’s circumference touches the reference globe’s surface along a great circle. The diameter of the cylinder is equal to the diameter of the globe. The tangent line is the equator for the equatorial or normal aspect; while in the transverse aspect, the cylinder is tangent along a chosen meridian
In the secant case, the cylinder intersects the globe; that is the diameter of the cylinder is smaller than the globe’s. At the place where the cylinder cuts through the globe two secant lines are formed.
3. Distortion- Areas that are most distorted?
4. There is more than one version?
Yes, there is the Transverse Mercator projection which is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection. The transverse version is widely used in national and international mapping systems around the world, including the UTM.
5. Problems?
The main problem is that this projection gives to people a false impression of the size of the world’s country. Another problem is that another projection could have been used instead of using it, as it would have been more appropriate and would have had a smaller margin of error. And the last problem is that this projection makes larger some continents than another, thus it can be use in the benefice of the powerful colonies.
6. Socio-Cultural Implications of using it as a learning resource?
As this projection makes the areas bigger than they actually are, it can be a problem because children will grow up thinking some places aren’t as important. Taking into account what said Salvatore Natoli (“In our society we unconsciously equate size with importance and ever power”), people use to underestimate the true size of the continent which were minimized relative to places that they view as more important or more powerful. Another problem is that it creates an ethnic prejudice against the third world since it places Europe in the middle of the map and it makes smaller Africa.
Robinson’s projection.
1. Purpose.
It was created specifically by the aim to find a good consensus to the problem of showing easily the complete globe in a flat image.
2. Distortion types.
This type of projection has the four different distortions: shape, area, distance and direction.
Shape: Feature outlines (like country boundaries) look the same on the map as they do on the earth. This kind of map is called conformal. But for more than a map is conformal, shapes are a bit distorted for very large areas, like continents.
Area: consist of the size of a feature on a map which is the same relative to its size on the earth.
Distance: consist of if the scale of the map is true or not. We can say that it is a true scale (equidistant map) when a line from a to b on a map is the same distance (accounting for scale) that it is on the earth.
Direction: also called azimuth, it is consist of the measure of the angle between a and b. This create an angle between the meridian on which a lies and the great circle arc connecting a to b.
3. Distortion- Areas that are most distorted?
It is possible to estimate a severe distortion in the poles, but rapidly it goes on to moderate levels as we are moving away from them. As in the poles, a severe angular distortion appears in the high latitudes near the margins of the map.
All points have some distortion but it is very low along the equator and within 45º of centre.
4. There is more than one version?
No, there isn’t.
5. Problems
Area, shape, distance and direction are not accurate.
Meridians are gently curved, avoiding extremes.
Stretches the poles; severe distortion close to the poles.
6. Socio-Cultural implications of using it as a learning resource
We use this type of projection because it has a better balance between size and shape of high-latitude lands, which it allow us to see the world more close to the reality than with other projections.
COUNTRY DESCRIPTION.
We have chosen Bolivia, in South-America, and Poland, Europe, in order to explain an evidence of distortions in the maps within different projections.
In the Robinson’s projection: we can observe that although the total area of Poland is smaller than Bolivia, in the Robinson’s projection it is the same, so we can affirm that the Robinson’s Projection is well represented.
In the Mercator’s projection: In the present maps we can observe that the surface of Poland is smaller than the one of Bolivia; and if we look at the projection of Mercator, we can see that the same thing happens; Bolivia is greater than Poland; so we can ensure that this type of map is not so bad after all.
In the Azimuthal’s projections: the projection centre is placed on the equator, and it’s focus on Africa, in this way Poland and Bolivia are in their right positions, with their almost accurate proportions.
BEST PROJECTIONS
We have chosen Robinson’s projection because we all consider that it offers a very clear image of the Earth, in which we can appreciate without any problem where and as it is each country, since despite a slight distortion as we get closer to the poles. The center (Ecuador) is well represented without any distortion. This allows children to easily and directly appreciate all the continents and countries that make up the world and compare their sizes in a correct way.
Although we first thought of choosing the Azimuthal projection, thus there is hardly any distortion, it was quickly discarded so it is not possible to see clearly where and how each country is, since they appear all blurred and it is not specified which is, making it difficult for children to understand this type of map.
TREASURE HUNT
We create an treasure Hunt and we search for another which is still made.
Our Treasure Hunt consists of a series of activities / challenges that children in 5th grade must overcome by applying the knowledge they have acquired during Mathematics, Language, English and Social Science classes.
Before beginning the activity, the tutors of the course will ask that the children be placed in groups of 5 and will be given to each one a map in which will be detailed the places in which they will have to look for the clues. Well, in the first challenge they will have to choose one of them to perform 5 mathematical operations, after this they will be given the clue that will lead them to the next challenge; The next activity that they will have to do will be in group and they will have to form 5 words related with language in a limited time without being allowed the repetition of some of them. Then, in the next challenge, they will be presented with the images of the planets of the solar system, they will have to relate the names with the images and order the planets according to the position that they occupy with respect to the Sun; Later they would pass to the activity in which the written track will be found upside down and the teacher should tell him that he needs an object that they must guess with the following riddle:
“When I look to you, you are looking to me;
When you are looking to me, I see you
And I am not ugly to you.
It’s true you are seeing it,
It’s false it sees you,
Both of you are similar,
It’s clear that you are him.
Who looks at me is reflected
so no one will have a complaint.
Very nice ahead
And very ugly from behind;
I transform myself every moment,
I imitate others”
And after passing that test they will have to face a last challenge, in which they will encounter pieces of puzzle that they must assemble and thus they will give with the last clue that will take them to the place where the treasure is.
And this is the treasure Hunt that we choose from internet.
Sample Treasure Hunt Clues
Hello everyone!
It’s time to look for the clues
Everyone jump up and yell WAHOO!!!
Look under stairs for clue #2!
Jump for Glee
When You Find Clue #3
Under the Birdbath,
It Will Be!!
Are You Ready To Go,
Out by the Garage Door,
Sitting On The Chair is Clue #4
For #5 To The Back of the Yard We Go,
Under the bucket, Oh No!
By the Compost Pile.
Don’t worry — it’s not a mile!
Clue #6 Is under the fireplace in the fort.
Don’ t Worry About Finding It,
It Really Won’t Be Hard!
Don’t Bonk Your Head!
Clue #7 is Under The Deck.
Be Careful When You Look, it’s hanging on the wall.
The treasure, Where is it Found?!
Run Quick, but not too hard
Out to the Front Yard!
For this game, all of the clues were in the back yard of the house and the treasure was in the front yard. We made bags of assorted candy for each child so that everyone who attended the game received a gift bag at the end of the treasure hunt. Adapt this concept to your own class and they will have lots of fun!
https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/treasure-hunt
DISTORTION IN MEDIA
Increasingly young girls are influenced by the media, such as television or magazines. In them they appear some canons of beauty that are not real, but nevertheless they wish to be like the women who see in those means, and if they fulfill them they consider that they will not be accepted by their friends, who are going to be marginalized and inferior to the rest, creating a feeling of self-rejection and preventing them from accepting themselves as they are.
On the contrary, the boys are not so influenced by the mass media despite the existence of stereotypes towards them such as good physical condition. This is due to the fact that society and especially the media do not criticize them as much as they do, nor do they consider that they will not be accepted in their groups of friends.
The influence of the media can be seen everywhere, from how we dress to how we act and this is what we want to demonstrate by example, which happened in real life, about the process of transformation of a sixth-girl from elementary school.
Lia, a girl from sixth grade had a best friend since her childhood, called Lili. These were childhood friends, always were and did everything together. However, entering sixth grade Lili changed. He began to watch television programs that were considered unfit for his age causing a great change in her. Little by little she began to focus more on her image, that to put on, if she went out with many boys would be the most popular, as if she was in sexy clothes, which was not appropriate for her age. This produced such a radical change in Lili that Lia and she left unhappily to be friends.





No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario